Further Than Before: Pathway To The Stars, Tome (Parts 1 & 2 Combined!)
Further than Before: Pathway to the Stars, Tome (Parts 1 & 2 Combined!)
View this post on Instagram
Combined as one! Further than Before: Pathway to the Stars, Parts 1 & 2 in an 8.3 x 11.7 inch novel of 400K words that hit the intellect in the best and most sophisticated ways,… through #scifi #fantasy #mustread #physics #theoreticalphysics #spaceopera #strongfemalelead #strongmalerolemodel #physiology #neuroscience #nanotechnology…
View On WordPress
More Posts from Matthewjopdyke and Others
10 Things: Journey to the Center of Mars
May the fifth be with you because history is about to be made: As early as May 5, 2018, we’re set to launch Mars InSight, the very first mission to study the deep interior of Mars. We’ve been roaming the surface of Mars for a while now, but when InSight lands on Nov. 26, 2018, we’re going in for a deeper look. Below, 10 things to know as we head to the heart of Mars.

Coverage of prelaunch and launch activities begins Thursday, May 3, on NASA Television and our homepage.
1. What’s in a name?

“Insight” is to see the inner nature of something, and the InSight lander—a.k.a. Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport—will do just that. InSight will take the “vital signs” of Mars: its pulse (seismology), temperature (heat flow) and reflexes (radio science). It will be the first thorough check-up since the planet formed 4.5 billion years ago.
2. Marsquakes.
You read that right: earthquakes, except on Mars. Scientists have seen a lot of evidence suggesting Mars has quakes, and InSight will try to detect marsquakes for the first time. By studying how seismic waves pass through the different layers of the planet (the crust, mantle and core), scientists can deduce the depths of these layers and what they’re made of. In this way, seismology is like taking an X-ray of the interior of Mars.
Want to know more? Check out this one-minute video.
3. More than Mars.

InSight is a Mars mission, but it’s also so much more than that. By studying the deep interior of Mars, we hope to learn how other rocky planets form. Earth and Mars were molded from the same primordial stuff more than 4.5 billion years ago, but then became quite different. Why didn’t they share the same fate? When it comes to rocky planets, we’ve only studied one in great detail: Earth. By comparing Earth’s interior to that of Mars, InSight’s team hopes to better understand our solar system. What they learn might even aid the search for Earth-like planets outside our solar system, narrowing down which ones might be able to support life.
4. Robot testing.
InSight looks a bit like an oversized crane game: When it lands on Mars this November, its robotic arm will be used to grasp and move objects on another planet for the first time. And like any crane game, practice makes it easier to capture the prize.
Want to see what a Mars robot test lab is like? Take a 360 tour.
5. The gang’s all here.

InSight will be traveling with a number of instruments, from cameras and antennas to the heat flow probe. Get up close and personal with each one in our instrument profiles.
6. Trifecta.

InSight has three major parts that make up the spacecraft: Cruise Stage; Entry, Descent, and Landing System; and the Lander. Find out what each one does here.
7. Solar wings.
Mars has weak sunlight because of its long distance from the Sun and a dusty, thin atmosphere. So InSight’s fan-like solar panels were specially designed to power InSight in this environment for at least one Martian year, or two Earth years.
8. Clues in the crust.

Our scientists have found evidence that Mars’ crust is not as dense as previously thought, a clue that could help researchers better understand the Red Planet’s interior structure and evolution. “The crust is the end-result of everything that happened during a planet’s history, so a lower density could have important implications about Mars’ formation and evolution,” said Sander Goossens of our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
9. Passengers.

InSight won’t be flying solo—it will have two microchips on board inscribed with more than 2.4 million names submitted by the public. “It’s a fun way for the public to feel personally invested in the mission,” said Bruce Banerdt of our Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the mission’s principal investigator. “We’re happy to have them along for the ride.”
10. Tiny CubeSats, huge firsts.

The rocket that will loft InSight beyond Earth will also launch a separate NASA technology experiment: two mini-spacecraft called Mars Cube One, or MarCO. These suitcase-sized CubeSats will fly on their own path to Mars behindInSight. Their goal is to test new miniaturized deep space communication equipment and, if the MarCOs make it to Mars, may relay back InSight data as it enters the Martian atmosphere and lands. This will be a first test of miniaturized CubeSat technology at another planet, which researchers hope can offer new capabilities to future missions.
Check out the full version of ‘Solar System: 10 Thing to Know This Week’ HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

2020 February 19
UGC 12591: The Fastest Rotating Galaxy Known Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble; Processing & Copyright: Leo Shatz
Explanation: Why does this galaxy spin so fast? To start, even identifying which type of galaxy UGC 12591 is difficult – featured on the lower left, it has dark dust lanes like a spiral galaxy but a large diffuse bulge of stars like a lenticular. Surprisingly observations show that UGC 12591 spins at about 480 km/sec, almost twice as fast as our Milky Way, and the fastest rotation rate yet measured. The mass needed to hold together a galaxy spinning this fast is several times the mass of our Milky Way Galaxy. Progenitor scenarios for UGC 12591 include slow growth by accreting ambient matter, or rapid growth through a recent galaxy collision or collisions – future observations may tell. The light we see today from UGC 12591 left about 400 million years ago, when trees were first developing on Earth.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap200219.html

My #mom went to be with my #dad yesterday morning. I will miss her dearly. #togetherforever they gave myself and siblings a home of #love and #kindness and they #taught us to be #loving and #kind I'll miss you both 💖 https://www.instagram.com/p/BvUjmvOAaac/?utm_source=ig_tumblr_share&igshid=1xk08dpggqtaz










Ask Ethan: How Does Very-Long-Baseline Interferometry Allow Us To Image A Black Hole?
“[The Event Horizon Telescope] uses VLBI. So what is interferometry and how was it employed by [the Event Horizon Telescope]? Seems like it was a key ingredient in producing the image of M87 but I have no idea how or why. Care to elucidate?”
If it were easy to network radio telescopes together across the world, we’d have produced an image of a black hole’s event horizon long ago. Well, it’s not easy at all, but it is at least possible! The technique that enabled it is known as VLBI: very-long-baseline interferometry. But there are some critical steps that aren’t very obvious that need to happen in order for this method to succeed. Remarkably, we learned how to do it and have successfully employed it, and the Event Horizon Telescope marks the first time we’ve ever been able to get an image with a telescope that’s effectively the size of planet Earth!
Come get the incredible science behind how the technique of VLBI enabled the Event Horizon Telescope to construct the first-ever image of a black hole’s event horizon!
Pathway to the Stars: Part 1, Vesha Celeste
Pathway to the Stars: Part 1, Vesha Celeste
Soon to be released, is the first in a latched-on (or related) series, Pathway to the Stars: Part 1, Vesha Celeste. This will be a slightly more descriptive portion that goes into more detail of the first character introduced, Vesha Celeste. Please pre-order, read, review, comment, and enjoy! Thank you!
Vesha Celeste journeys with Yesha Alevtina and her dream-angel, Sky, following a long life of…
View On WordPress









NASA Kepler’s Scientists Are Doing What Seems Impossible: Turning Pixels Into Planets
“It isn’t the image itself that gives you this information, but rather how the light from image changes over time, both relative to all the other stars and relative to itself. The other stars out there in our galaxy have sunspots, planets, and rich solar systems all their own. As Kepler heads towards its final retirement and prepares to be replaced by TESS, take a moment to reflect on just how it’s revolutionized our view of the Universe. Never before has such a small amount of information taught us so much.”
When you think about exoplanets, or planets around stars other than the Sun, you probably visualize them like we do our own Solar System. Yet direct images of these worlds are exceedingly rare, with less than 1% of the detected exoplanets having any sort of visual confirmation. The way most planets have been found has been from the Kepler spacecraft, which gives you the very, very unimpressive image of the star you see featured at the top. Yet just by watching that star, the light coming from it, and the rest of the field-of-view over time, we can infer the existence of sunspots, flares, and periodic “dips” in brightness that correspond to the presence of a planet. In fact, we can figure out the radius, orbital period, and sometimes even the mass of the planet, too, all from this single point of light.
How do we do it? There’s an incredible science in turning pixels into planets, and that’s what made NASA’s Kepler mission so successful!
Pretty nice representation of Earth on through to the observable universe

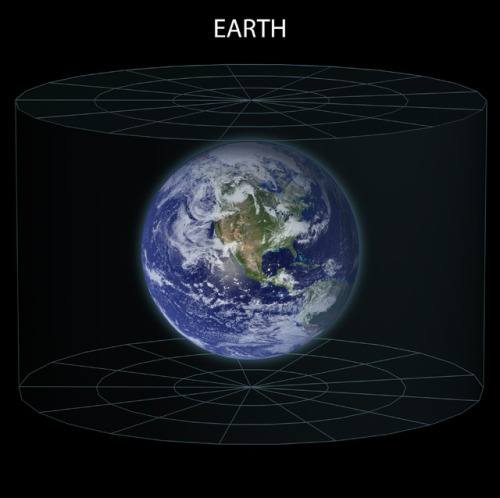
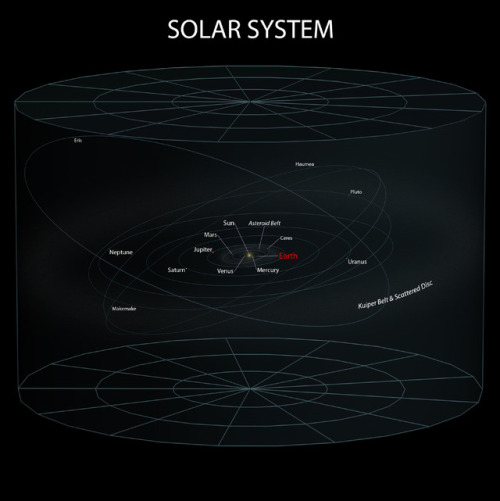
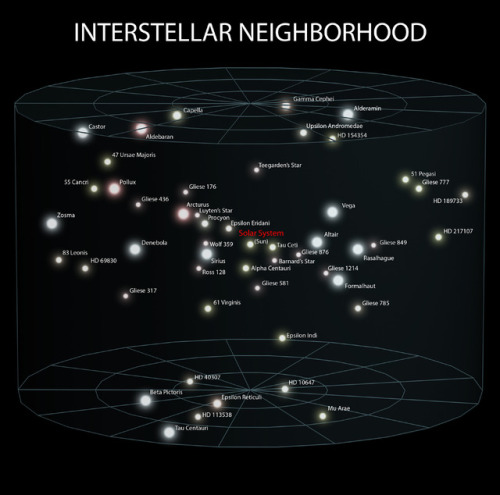

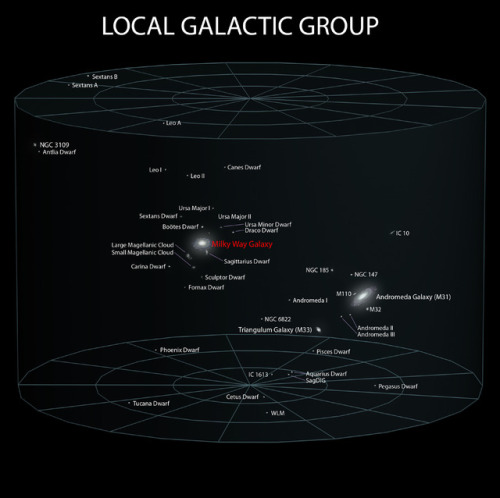
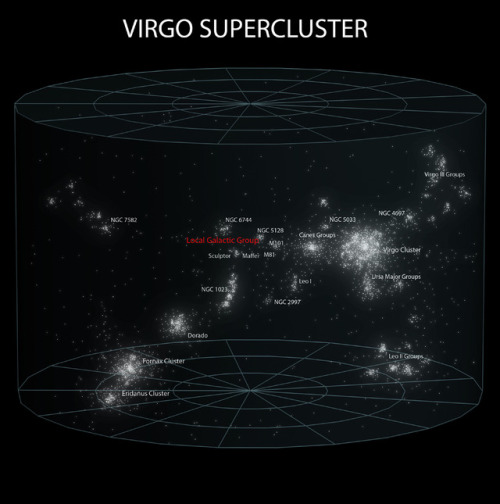
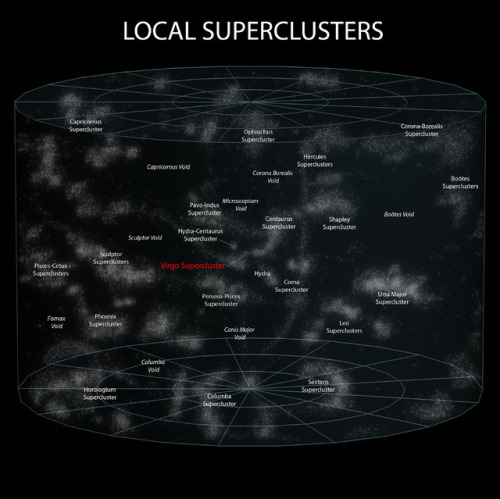

~ wikimedia commons
A Cosmic Legacy: From Earth to the Stars (Extended Video)
"Our beautiful mother world ached for a reprieve from the injustices of many, courtesy of cultures and governance systems, that forgot how to love, how to be kind, how to include others, and how to think beyond the scope of greed and power, but within the visions of shared joy and well-being."
“For far too long people have lived for merely one shared goal, due to the daunting nature that life seems to bring. That goal may be a noble one, but it comes short of progression in and of itself and does not recognize the complexity of life and all of its nuances.
“This goal is survival through natural evolution. To merely survive, no matter the means, as noble as it may seem at first, will actually lead to the end of life and the end of humanity, whether through natural events or mankind’s apparent affinity toward death.
“It’s as if far too many people worship the almighty ‘mixed result’ rather than raise the quality of and joy in life through logic, study, innovation, and common sense, by enjoying what it can bring to the table, which will ultimately result in desired results.
“Finding cures for disease, both physiological and neurological, and possessing the ingenuity to innovate technologies as well as a pathway for humanity to quicken their pace for developing them will lead to preserving our Earth, our solar system, perhaps our Universe, and with it, each individual and humanity itself, as we travel to and push the limits of the Universe and its sustainability, trusting ourselves as we do so.”
Enjoy this First-Year-Anniversary compilation of all of my works in one title: A Cosmic Legacy: From Earth to the Stars
This title includes the entire Pathway to the Stars series: Part 1, Vesha Celeste Part 2, Eliza Williams Part 3, James Cooper Part 4, Universal Party Part 5, Amber Blythe Part 6, Erin Carter Part 7, Span of Influence Part 8, Dreamy & Deep Part 9-Allure & Spacecraft Part 10-Sky Taylor Part 11-A New Day Part 12-Alpha Andromedae
Eliza Williams and a host of friendly heroes tackle some of the most significant dilemmas of the day to bring humanity out and into the stars bearing a legacy we would be proud to share with other civilizations--a legacy of kindness, of mind-to-mind communication, of love, and of healing instead of harming. If we are to overcome the great expansion and the death of all life, we must overcome the smaller challenges to progress and focus on even greater ones. Working with her team diligently, Eliza will speed the pace of society in her world with the belief that beauty and untold potential are within every being. If we find ways to bring that out in ourselves and others, a future where we can breed longevity, a collective and high quality of life, augment the clarity of our minds, and innovate to span the Cosmos may be in our grasp.
Together with the organization Eliza Williams founded, called Pathway, she and her growing team will take us on a fantastical and Utopian journey to get us out and into the farthest reaches of space. There are dilemmas such as the physiological effects of space on each of us, as well as the need for longevity and a desire to still be able to visit loved ones following long journeys. Eliza and her team develop capabilities, so we can overcome the challenges ahead and are determined to stabilize a rocky economy, wipe away suffering, violence, disease, cartels, terrorism, and trafficking in persons. They work together to tame seismic activity, weather, and fires. She and her friends tackle ways to prevent extinction and provide solutions to quality of life concerns. They even consider the longevity of our Sun and our Earth's capacity to preserve life. Eliza tackles each of these issues to get us out, and into the stars, so we can begin our biggest quest--to help our Universe breathe ever so lightly.
No matter the challenge, there will always be greater pursuits! The saga will continue...
"A Cosmic Legacy" is a science fiction & fantasy novel, with a Space Opera flair to it. It is designed to edify, educate, and entertain young adults and scholars alike. Some of the specific topics covered include physiology, neurology, physics, biotechnology, nanotechnology, astronomy, politics, philosophy, and ethics. Preservation of the life-giving and sustaining capacities of our Earth and creation of environments conducive to life throughout the Solar System once thought to be impossible are primary goals. The ideas of kindness, with innovation rooted in well-being, longevity, where cellular health expresses youth and rejuvenation, optimizing the body to be able to live comfortably in austere space environments without adverse effects, and mind-to-mind communication bearing with it a legacy we'd be proud to share with distant civilizations with mutual goals of preserving our Universe can bring a beautiful future for all living beings.
Hardcover (Regular price $45) LCCN: 2019911854 | ISBN: 978-1-7333131-2-4 https://smile.amazon.com/dp/1733313125
Paperback (Regular price $35) LCCN: 2019909638 | ISBN: 978-1-7333131-1-7 https://smile.amazon.com/dp/1733313117
eBook (Regular price $10) LCCN: 2019909630 | ISBN: 978-1-7333131-0-0 | ASIN: B07V4W3MW9 https://smile.amazon.com/dp/B07V4W3MW9
#scifi #fantasy #spaceopera #newideology #wellbeing #longevity #neuroscience #neurotech #physiology #biology #biotech #physics #theoreticalphysics #nanotech #CRISPR #stemcellresearch #innovation #positivity #clarityofmind #author #matthewjopdyke #books #novels #ebooks #space #stars #astronomy #stem #science #ethicalrolemodels #universalethics

(NASA) Unexpected X-Rays from Perseus Galaxy Cluster
Image Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXO/Oxford University/J. Conlon et al.; Radio: NRAO/AUI/NSF/Univ. of Montreal/Gendron-Marsolais et al.; Optical: NASA/ESA/IoA/A. Fabian et al.; DSS
Why does the Perseus galaxy cluster shine so strangely in one specific color of X-rays? No one is sure, but a much-debated hypothesis holds that these X-rays are a clue to the long-sought identity of dark matter. At the center of this mystery is a 3.5 Kilo-electronvolt (KeV) X-ray color that appears to glow excessively only when regions well outside the cluster center are observed, whereas the area directly surrounding a likely central supermassive black hole is actually deficient in 3.5 KeV X-rays. One proposed resolution – quite controversial – is that something never seen before might be present: florescent dark matter (FDM). This form of particle dark matter might be able to absorb 3.5 KeV X-radiation. If operating, FDM, after absorption, might later emit these X-rays from all over the cluster, creating an emission line. However, when seen superposed in front of the central region surrounding the black hole, FDM’s absorption would be more prominent, creating an absorption line. Pictured, a composite image of the Perseus galaxy cluster shows visible and radio light in red, and X-ray light from the Earth-orbiting Chandra Observatory in blue.
Source

Thank you for your endless curiosity Dr. Hawking.
